Most Common Causes of Toothaches
How to Prevent Gum Disease with Gum Disease Therapy
Best Cosmetic Dentistry in Coraopolis, PA
Toothaches can be incredibly disruptive, affecting your ability to eat, sleep, and focus on daily activities. While the pain can range from mild to severe, understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common causes of toothaches and how to manage and prevent them.
1. Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, or cavities, is one of the most common causes of toothaches. When plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—builds up on your teeth, it produces acids that erode the tooth enamel. Over time, this erosion can create holes in the teeth, leading to pain, especially when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
Prevention and Management:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and flossing daily.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride helps strengthen enamel and prevent decay.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups to catch decay early.
- Reduce Sugar Intake: Limit sugary foods and drinks that contribute to plaque formation.
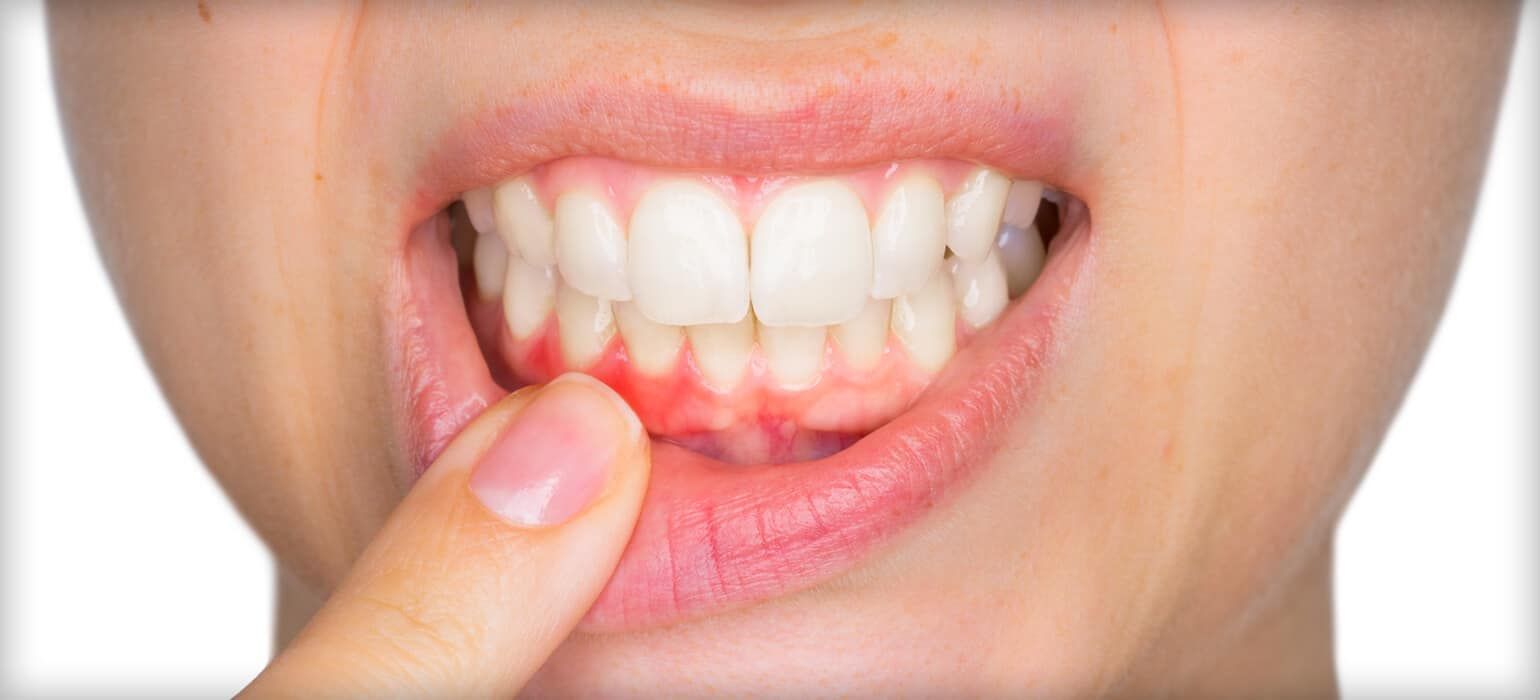
2. Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that can lead to toothaches. It starts with gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected.
Prevention and Management:
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to remove plaque and food particles.
- Regular Dental Visits: Professional cleanings help remove tartar that can’t be eliminated by brushing alone.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of gum disease.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet to support gum health.
3. Tooth Abscess
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection, usually resulting from untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or a cracked tooth. Abscesses can cause severe, throbbing pain that radiates to the jaw, neck, or ear, along with swelling, fever, and a bad taste in the mouth.
Prevention and Management:
- Seek Immediate Dental Care: If you suspect an abscess, see your dentist right away. Delaying treatment can lead to serious complications.
- Root Canal Treatment: This procedure removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth to prevent further infection.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate the infection.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Prevent abscesses by keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
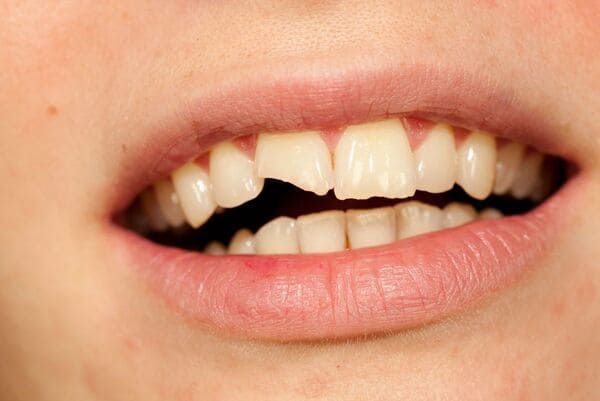
4. Tooth Fracture
A cracked or fractured tooth can cause pain when chewing, biting, or exposing the tooth to temperature extremes. Fractures can result from trauma, biting down on hard foods, or grinding your teeth at night.
Prevention and Management:
- Wear a Mouthguard: If you play contact sports or grind your teeth, a mouthguard can protect your teeth from injury.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Be cautious with hard foods like nuts, ice, and hard candies.
- Dental Treatment: Depending on the severity, treatment may involve bonding, a crown, or a root canal. In severe cases, the tooth may need to be extracted.
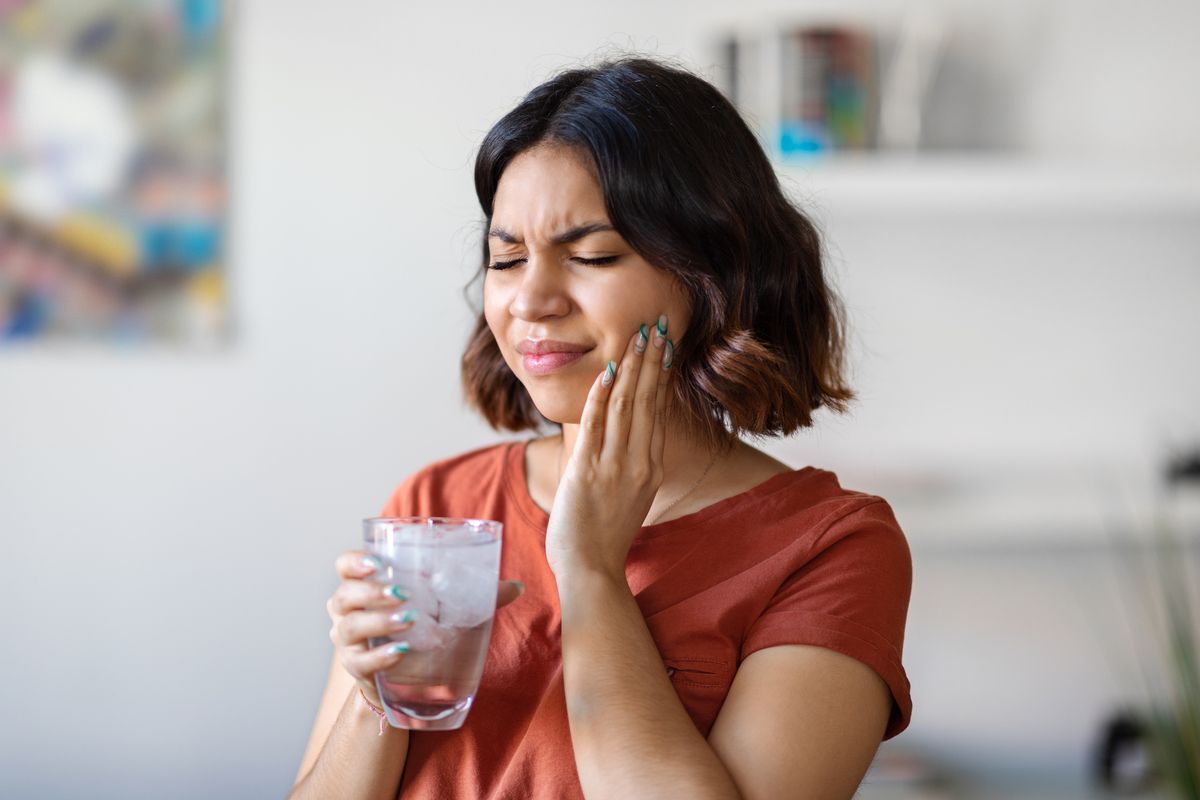
5. Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity can cause sharp pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. This sensitivity occurs when the enamel wears down, exposing the underlying dentin or when gum recession exposes the tooth roots.
Prevention and Management:
- Use Desensitizing Toothpaste: These toothpastes contain compounds that help block pain signals to the nerves.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Limit consumption of acidic foods and drinks that can erode enamel.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Brush with a soft-bristled toothbrush and use fluoride toothpaste.
- Dental Treatments: Your dentist may apply fluoride gel or recommend other treatments to reduce sensitivity.
6. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Bruxism is the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth, often during sleep. It can cause toothaches, jaw pain, and headaches. Over time, bruxism can wear down tooth enamel and cause fractures.
Prevention and Management:
- Wear a Nightguard: A custom-fitted nightguard can protect your teeth while you sleep.
- Stress Management: Reduce stress through relaxation techniques, as stress is a common trigger for bruxism.
- Dental Correction: If misaligned teeth are causing bruxism, orthodontic treatment may be necessary.
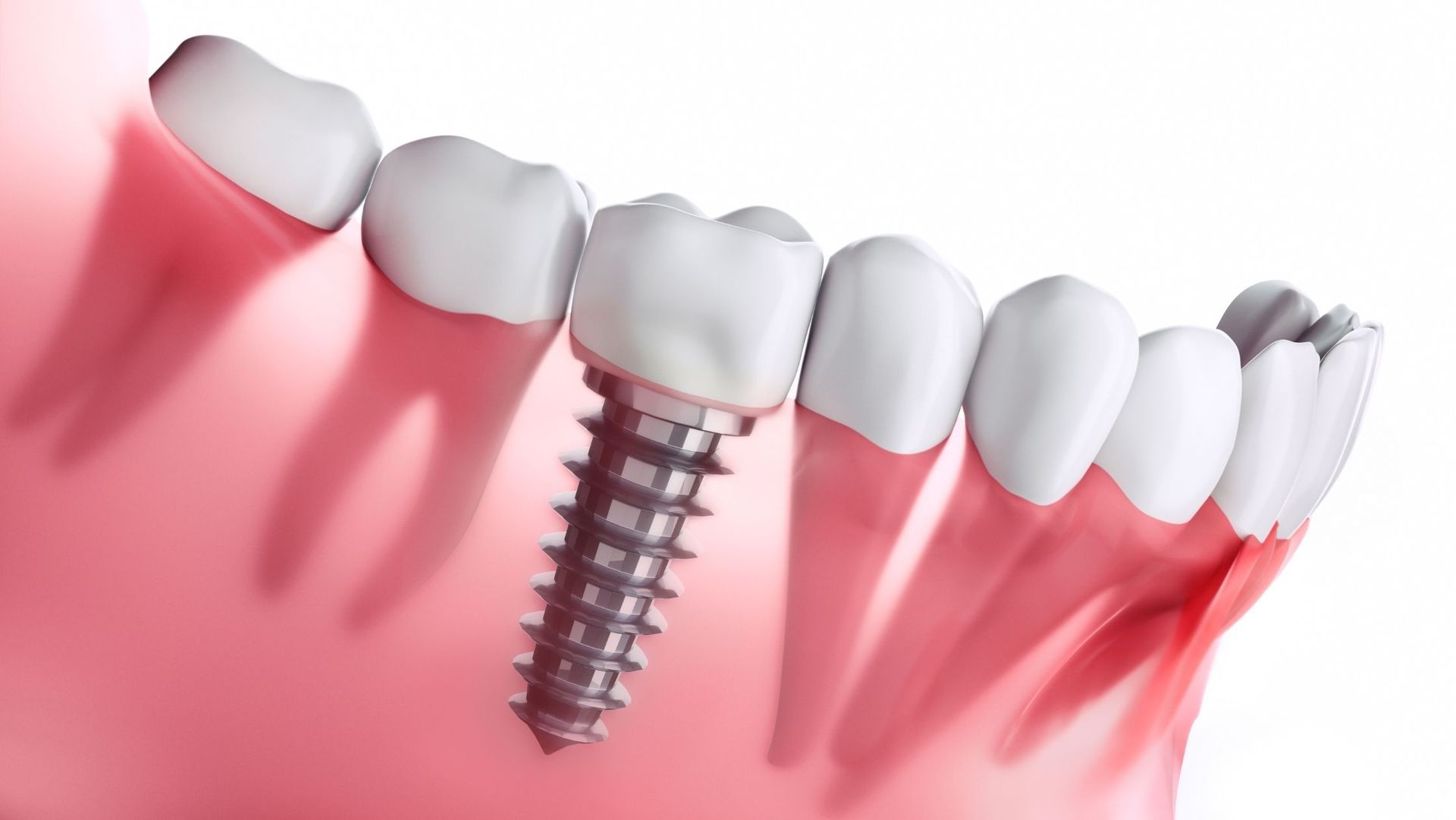
7. Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth, the last set of molars to develop, can cause pain when there isn’t enough space for them to emerge properly. This can lead to swelling, infection, and damage to adjacent teeth.
Prevention and Management:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Monitor the development of wisdom teeth with regular dental visits.
- Extraction: If impacted, your dentist may recommend extracting the wisdom teeth to prevent complications.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers and saltwater rinses can help manage pain and inflammation.
8. Sinus Infections
Sinus infections can cause referred pain to the upper teeth due to their proximity to the sinus cavities. If you experience tooth pain along with sinus congestion, pressure, and a headache, a sinus infection might be the cause.
Prevention and Management:
- Treat the Sinus Infection: Consult your doctor for appropriate treatment, which may include decongestants, antihistamines, or antibiotics.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to thin mucus and relieve sinus pressure.
- Nasal Irrigation: Use a saline solution to rinse your nasal passages and reduce congestion.
9. Dental Procedures
Recent dental procedures, such as fillings, crowns, or extractions, can cause temporary toothaches. This pain is usually due to inflammation or sensitivity in the affected area.
Prevention and Management:
- Follow Post-Procedure Instructions: Adhere to your dentist’s instructions for care after a dental procedure.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort.
- Contact Your Dentist: If pain persists or worsens, contact your dentist to ensure there are no complications.
Understanding the common causes of toothaches is the first step in managing and preventing this painful condition. Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and addressing any dental issues promptly can help keep your teeth and gums healthy. If you experience a toothache, don’t ignore it—seek professional dental care to identify the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
66 Forest Grove Rd Coraopolis, PA 15108